Spotlight
Letter from Dr. Stephen I. Katz: NIH Announces Funding Opportunities Through the Accelerating Medicines Partnership
In today’s research environment, candidate drugs are increasingly being developed based on their effects on biological targets of disease. However, many of the drug candidates that show promise in early-stage research are found to be ineffective during later clinical testing. To transform the current model for identifying and validating promising biological targets for new diagnostics and drug development, the National Institutes of Health (NIH), 10 biopharmaceutical companies, the Foundation for the NIH, and several health advocacy organizations launched the Accelerating Medicines Partnership (AMP) in February 2014. The AMP will invest approximately $230 million over five years for research in three disease areas: Alzheimer’s disease, type 2 diabetes, and the autoimmune diseases rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The NIAMS, with leadership from Drs. Robert Carter and Susana Serrate-Sztein, has been a major contributor to the development and implementation of the autoimmune diseases effort, and this month’s letter highlights the AMP program in those areas.
Image: Stephen I. Katz, M.D., Ph.D.
News
Funding Opportunities for AMP Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lupus Program Now Available
Two funding opportunity announcements (FOAs) are now available under the Accelerating Medicines Partnership (AMP) for the Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lupus (RA/SLE) Program. The FOAs are requesting applications to establish Network Research Sites and a Network Leadership Center. AMP is a collaborative effort involving the NIH, pharmaceutical companies and nonprofit organizations to develop new models for identifying and validating promising biological targets for new diagnostics and drug development. A major goal is to generate precompetitive, disease-specific data that will be publicly accessible to the broad biomedical community for further research.
A working draft of the AMP RA/SLE Project Plan is available, along with frequently asked questions (FAQ’s).
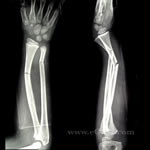
Childhood Forearm Breaks Resulting from Mild Trauma May Indicate Bone Deficits
Children who break their forearm after just a mild trauma may have underlying bone health conditions, according to recent research funded in part by the NIAMS, and published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. Optimal bone development is dependent on a complex interplay of genetic, hormonal, environmental, and behavioral factors. Although there is some evidence that childhood fractures may suggest skeletal fragility, it is also possible that these fractures are simply a consequence of energetic childhood activities.
Image: X-ray image of a child’s forearm fracture. Photo credit: eORIF LLC.
Spinal Stimulation Helps Four Patients with Paraplegia Regain Voluntary Movement
Four people with paraplegia are able to voluntarily move previously paralyzed muscles as a result of a novel therapy that involves electrical stimulation of the spinal cord, according to a study funded in part by the NIH and the Christopher & Dana Reeve Foundation. The participants, each of whom had been paralyzed for more than two years, were able to voluntarily flex their toes, ankles, and knees while the stimulator was active, and the movements were enhanced over time when combined with physical rehabilitation. Researchers involved in the study say the therapy has the potential to change the prognosis of people with paralysis even years after injury.
NIH Opens Research Hospital to Outside Scientists: New Program Tackles Disease on Many Fronts
Ten projects that will enable non-government researchers to conduct clinical research at the NIH’s Clinical Center in Bethesda, Md. have been announced. Through these three-year, renewable awards of up to $500,000 per year, scientists from institutions across the United States will collaborate with government scientists in a highly specialized hospital setting. The NIH Clinical Center is the largest hospital in the nation devoted entirely to clinical research.
NIH Celebrates Grand Opening of John Edward Porter Neuroscience Research Center: State-of-the-Art Research Facility on NIH Campus Will Foster New Collaborations Among Scientists Studying the Brain
The NIH hosted a scientific symposium and a dedication ceremony to celebrate the completion of the John Edward Porter Neuroscience Research Center. This state-of-the-art facility brings together neuroscientists from 10 Institutes and Centers across the NIH in an effort to spur new advances in our understanding of the nervous system in health and disease.
Human Subjects Training for Physicians
Some of you may have taken human subjects training offered at your home institution, but did you know the NIH offers free online training as well? Since 2008, the NIH’s Office of Extramural Research has offered the Protecting Human Research Participants(PHRP) course to all researchers seeking information on the ethical conduct of research involving human subjects. Each year, more than 200,000 individuals complete this training, which is offered in both English and Spanish. The course is just one way grantees can meet the NIH’s education requirement on the protection of human subjects.
More on Big Data Training for the Scientific Workforce
Biomedical science and healthcare research are generating increasingly large and complex sets of data, from many different subfields. New strategies are needed to manage, integrate, analyze, visualize and draw conclusions from this “big data.” Our Big Data to Knowledge (BD2K) Initiative, which originated from an Advisory Committee to the Director (ACD) working group, is the NIH’s way of addressing these needs.
NIH Director’s Blog
Antimicrobial Resistance: Seeing the Problem at Hand
You’ll be relieved to know that this is not a real hand, swarming with exotic species of microbes. But this eerie image does send a somber message: antimicrobial resistant bacteria (green) are becoming more common and more resilient, while the numbers of vulnerable bacteria (red) are dwindling.
Image: Credit: Lydia-Marie Joubert, Stanford University Medical Center
Other Federal News
Can a Massage Be Beneficial for Your Health?
Massage is among the top ten most frequently used complementary health practices by adults and by children. While often preliminary or conflicting, much of the scientific evidence points toward beneficial effects on pain and other symptoms associated with a number of different conditions.
The myhealthfinder Tool at Healthfinder.gov Tells You Which Screening Tests You May Need
Screenings are medical tests that check for diseases before there are any symptoms. Screenings can help doctors find diseases early, when the diseases may be easier to treat. Getting a screening test is one of the most important things you can do for your health. Find out which preventive services you may need this year by using the myhealthfinder tool and entering your basic information, like age and sex. You can also use the myhealthfinder tool to find out about services recommended for a loved one.
FDA Patient Representative Program
You can participate in the Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) important decisions about the regulation of medical products in many ways. You don’t have to be an expert, and you don’t need to dedicate lots of time. Add your voice to FDA processes about important medical product development, review and policy questions.
NEW PUBLICATIONS
Categorical Spending Tables Updated in NIH RePORT
The NIH RePORT’s categorical spending tables—based on grants, contracts and other funding mechanisms used across the NIH—have been updated to reflect FY 2013 results from the Research, Condition, and Disease Categories (RCDC) database. The FY 2014/2015 estimates for 237 publically reported RCDC categories are also available.
NIH Research Matters
NIH Research Matters is a review of NIH research from the Office of Communications and Public Liaison, Office of the Director, NIH.
Physical Activity Brings Lasting Bone Benefits
A study of professional baseball players showed that some benefits of building bone during youth can last a lifetime. The research also confirmed that continued physical activity can help maintain bone strength as we age.
Electroacupuncture Reduces Sepsis in Mice
Researchers found that electroacupuncture in mice reduced the inflammation responsible for sepsis. The mechanisms underlying the therapy hint at new approaches to treat inflammatory disorders.
NIH News in Health
Read practical health information in NIH News in Health, which is reviewed by the NIH’s medical experts and is based on research conducted either by the NIH’s own scientists or by its grantees at universities and medical schools around the country.
MEETINGS
NIAMS Advisory Council Meeting
The NIAMS Advisory Council Meeting will be held June 3, 2014, in Building 31, 6th Floor, C Wing, Conference Room 6, NIH Campus. A meeting agenda will be posted as soon as it is available.

NIH Wednesday Afternoon Lecture Series
The NIH’s Wednesday Afternoon Lecture Series offers weekly lectures every Wednesday at 3 p.m. in Masur Auditorium, Building 10, NIH Campus. Renowned scientists from around the globe present research on a variety of topics. The lectures are Continuing Medical Education-certified, open to the public and available live via webcast.
Upcoming Lectures:
April 30, 2014
Peter Palese, The Mount Sinai Hospital
“Toward a Universal Influenza Virus Vaccine”
May 14, 2014
The Annual R. E. Dyer Lecture
Akiko Iwasaki, Yale School of Medicine
“Antiviral Defense Mechanisms at the Mucosal Surfaces”
NIH Science Lectures and Events Available Online
The NIH hosts a number of science seminars and events that are available online through real-time streaming video. You can watch an event at your convenience as an on-demand video or a downloadable podcast. Most events are available to all; a few are broadcast for the NIH or the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and are marked as such. See additional details on events.
NIAMS Exhibit Schedule
The NIAMS exhibit is traveling to several events. See the schedule of health fairs and exhibits.
Image: The NIAMS Exhibit
FUNDING ANNOUNCEMENTS
NIAMS Announcements
Accelerating Medicines Partnership (AMP) in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lupus: Network Leadership Center (UM2)
(RFA-AR-14-015)
Letter of Intent Receipt Date: April 21, 2014
Application Receipt Date: May 21, 2014
Accelerating Medicines Partnership (AMP) in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Lupus: Network Research Sites (UH2/UH3)
(RFA-AR-14-016)
Letter of Intent Receipt Date: April 21, 2014
Application Receipt Date: May 21, 2014
Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award (NRSA) Individual Predoctoral Fellowship (Parent F31)
(PA-14-147)
Letter of Intent Receipt Date: Not applicable
Application Receipt Dates: Standard dates apply
Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award (NRSA) Individual Predoctoral Fellowship to Promote Diversity in Health-Related Research (Parent F31 - Diversity)
(PA-14-148)
Letter of Intent Receipt Date: Not applicable
Application Receipt Dates: Standard dates apply
Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award (NRSA) Individual Postdoctoral Fellowship (Parent F32)
(PA-14-149)
Letter of Intent Receipt Date: Not applicable
Application Receipt Dates: Standard dates apply
Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award (NRSA) Individual Predoctoral MD/PhD or Other Dual-Doctoral Degree Fellowship (Parent F30)
(PA-14-150)
Letter of Intent Receipt Date: Not applicable
Application Receipt Dates: Standard dates apply
Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Awards (NRSA) Individual Senior Fellowship (Parent F33)
(PA-14-151)
Letter of Intent Receipt Date: Not applicable
Application Receipt Dates: Standard dates apply
Early Stage Development of Technologies in Biomedical Computing, Informatics, and Big Data Science (R43/R44)
(PA-14-154)
Letter of Intent Receipt Date: Not applicable
Application Receipt Dates: Standard dates apply
Early Stage Development of Technologies in Biomedical Computing, Informatics, and Big Data Science (R01)
(PA-14-155)
Letter of Intent Receipt Date: Not applicable
Application Receipt Dates: Standard dates apply
Extended Development, Hardening and Dissemination of Technologies in Biomedical Computing, Informatics and Big Data Science (R01)
(PA-14-156)
Letter of Intent Receipt Date: Not applicable
Application Receipt Dates: Standard dates apply
Early Stage Development of Technologies in Biomedical Computing, Informatics, and Big Data Science (R41/R42)
(PA-14-157)
Letter of Intent Receipt Date: Not applicable
Application Receipt Dates: Standard dates apply
NIH Common Fund Initiative Announcements
Request for Information (RFI): Challenges and Opportunities in Understanding Genome Structure/Function Relationships
(NOT-RM-14-010)
Other Funding Announcements
Notice of Additional Legislative Mandate in Effect for FY2014 Restricting Pornography on Computer Networks
(NOT-OD-14-062)
Request for Information: Invitation To Comment on Proposed Guidance Regarding Significant Changes to Ongoing Animal Activities
(NOT-OD-14-063)
NIH Will Open the Research Performance Progress Report (RPPR) for All Type 5 Non-SNAP Progress Reports on April 25, 2014
(NOT-OD-14-064)
Notice of Online Data Submission and Access to the National Institutes of Health (NIH) database of Genotypes and Phenotypes (dbGaP)
(NOT-OD-14-065)
Notice of Implementation of Pilot Program for Enhancement of Employee Whistleblower Protections
(NOT-OD-14-068)
NIH Policy for Managing Conflict of Interest in the Peer Review of Concepts and Proposals for Research and Development Contract Projects
(NOT-OD-14-069)
Adjustments to May 25–28, 2014, Grant Application Due Dates
(NOT-OD-14-070)
NIH Extramural Grant Systems Upgrade for Unicode Compatibility Means Memorial Day Weekend Downtime
(NOT-OD-14-071)