SPOTLIGHT
Letter from Dr. Stephen I. Katz: NIAMS Improves Tools to Build Healthy Communities
Dear Colleagues,
In this new year, NIAMS is committed to continuing our work to improve the nation’s health and reduce illness and disability through research, training and information dissemination. As part of this commitment, we are taking steps to ensure that the health information we provide will truly make a difference in people’s lives. We are constantly looking for ways to empower organizations and community leaders that serve diverse populations with the health education tools they need.
We understand how important it is for community advocates and health professionals to have access to culturally and linguistically appropriate health information. To assist with these outreach efforts, NIAMS has created a new Community Outreach website. It features a large collection of information and resources on bones, joints, muscles and skin to help make health education activities a success. The site contains publications — categorized by disease type, lifespan, and sex and gender — that community intermediaries can tailor to their audiences. The new site also features social media sharing tools, including a set of eye-catching e-cards that can easily be shared with constituents to promote better health.
Image: Stephen I. Katz, M.D., Ph.D.
NEWS
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Joint-Specific Cell Differences Suggest the Need for Tailored Therapies
In a study funded in part by the NIAMS, researchers uncovered differences in key cellular processes between knee and hip joints of people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The findings suggest that tailoring RA medications to the affected joints in each individual could improve effectiveness and bring greater relief from symptoms.
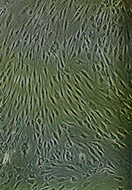
Image: Fibroblast-like synoviocytes reside in the joint lining and contribute to joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis.
Photo credit: Gary S. Firestein, M.D., University of California, San Diego.
Laura Lewandowski Studies Lupus in South African Children
As a Fogarty Fellow in South Africa, Laura Lewandowski, M.D., M.Sc.-G.H., studied pediatric lupus, which is more common and severe in people of African descent. In 2015, she joined the NIAMS as a Lawrence Shulman Scholar in Translational Medicine. As a clinical fellow in the NIAMS Systemic Autoimmunity Branch, her research focuses on the inflammation that drives lupus and whether genetic variants may cause some children to develop the autoimmune illness very early in life. She is also studying what causes people of African descent to suffer such a severe form of lupus.
Image: Dr. Laura Lewandowski studied pediatric lupus in South Africa during her Fogarty fellowship.
Photo credit: Karin Zeitvogel.
Muscle Aging Linked To Failure of Stem Cells To Interact With Environment
New research in mice, funded in part by NIAMS, has revealed that interactions between muscle stem cells and their immediate external environment deteriorate with aging, hampering muscle repair. The findings suggest that enhancing these connections could help maintain muscle strength in older adults and promote muscle repair in people with diseases such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
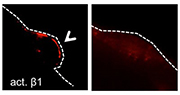
Image: Young satellite cells (left panel) carrying active β1-integrin (red) localize to the edge of a muscle fiber (dotted line). However, older cells (right panel) drift away from it, indicating the cells’ impaired function.
Photo credit: Chen-Ming Fan, Ph.D., Carnegie Institution for Science.
Tofacitinib Shows Potential for Treating Lupus
A drug that effectively treats rheumatoid arthritis and can improve symptoms in other autoimmune diseases may also control the symptoms associated with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE or lupus) and potentially slow the disease’s progression, according to a study in mice conducted by researchers at the NIAMS and published in the journal Arthritis and Rheumatology. The NIAMS investigators partnered with colleagues from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI) and the NIH’s Office of the Director.
Image: NIAMS researcher Dr. Massimo Gadina discusses the promise of using tofacitinib to treat lupus.
2016 Research Highlights
The NIH lists research accomplishments made by NIH-supported scientists in 2016. Several are related to the NIAMS mission.
Promising Medical Advances
Gene Editing Shows Promise in Different Disease Models
Gene-editing techniques, like CRISPR/Cas9, can successfully replace faulty genes, and scientists have been exploring their therapeutic potential. This year, NIH-funded scientists showed the approach holds promise as a gene therapy for three diseases in animal or cell models: Duchenne muscular dystrophy (in mice), sickle cell disease (in blood stem cells from affected people), and the inherited eye disorder retinitis pigmentosa (in rats).
Redefining Health and Well-Being in Older Adults
Researchers developed a “comprehensive model” to assess health that includes measures of health behaviors, psychological health, sensory function and frailty. One of the measures was bone fractures. The findings may help doctors better assess and manage the quality of life and health of older adults.
Clinical Breakthroughs
Meditation and Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy Ease Low Back Pain
Most people experience low back pain at some point in their lives. Treatment choices include over-the-counter and prescription drugs, cold and hot compresses, exercise, and in some cases, surgery. Researchers found that both mindfulness-based stress reduction and cognitive-behavioral therapy alleviated chronic low back pain in adults. The results validate more treatment options for people with back pain to consider with their health care providers.
NIH Director’s Blog: Talking Music and Science With Yo-Yo Ma
Dr. Collins writes, “It’s not every day that an amateur guitar picker gets to play a duet with an internationally renowned classical cellist. But that was my thrill this week as I joined Yo-Yo Ma in a creative interpretation of the traditional song, ‘How Can I Keep From Singing?’ Our short jam session capped off Mr. Ma’s appearance as this year’s J. Edward Rall Cultural Lecture.”
Image: Dr. Francis Collins (l) performs with Yo-Yo Ma.
FDA Approves First Autologous Cellularized Scaffold for the Repair of Cartilage Defects of the Knee
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Maci (autologous cultured chondrocytes on porcine collagen membrane) for the repair of symptomatic, full-thickness cartilage defects of the knee in adult patients. Maci is the first FDA-approved product that applies the process of tissue engineering to grow cells on scaffolds using healthy cartilage tissue from the patient’s own knee.
FDA Approves Eucrisa for Eczema
The FDA approved Eucrisa (crisaborole) ointment to treat mild to moderate eczema (atopic dermatitis) in patients 2 years of age and older.
RESOURCES
Explore NIAMS’ New Community Outreach Website!
The NIAMS is excited to announce the launch of our new Community Outreach Initiative website. The purpose of this website is to provide community organizers like you with easy-to-find information that is relevant to the people you serve. This website will connect you with free resources about bones, joints, muscles, and skin as you plan your outreach efforts and community events. We organized the information to make it easier for you to find the resources you need to educate your patients and community members. Further, to help you conduct outreach or promote health messages both in-person and digitally, we have included an e-Toolkit that helps you connect with us on several social media platforms.
Spotlight on Scientific Imagery: Muscle Function
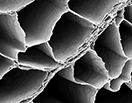
Composed primarily of collagen, connective tissue surrounds each individual muscle cell, creating a complex network. When an organism moves, the connective tissue helps transfer the force created by muscle cells to tendons and bones. This scanning electron microscopy image shows the connective tissue in a bullfrog’s leg muscle. The cells have been chemically digested away, leaving only collagen behind. The researchers are studying the structure of connective tissue from a variety of species to understand how it shapes muscle function. They also hope to learn how diseases that affect collagen structure influence muscle health. The NIH/NIAMS and the National Science Foundation provided funding for this research. This photo was selected as a 2016 winner of the BioArt competition of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB).
Image: The photo is courtesy of Thomas Roberts, Ph.D., and David Sleboda of Brown University.
Tai Chi and Your Health: A Modern Take on an Ancient Practice
You may have seen the flowing postures and gentle movements of tai chi. It is an ancient mind and body practice. While more research is needed, studies suggest that it may have many health benefits. Several studies have found evidence that tai chi can increase balance and stability in older people and reduce the risk and fear of falls. An online video about tai chi can be found here.
Study Shows Tai Chi and Physical Therapy Were Equally Helpful for Knee Osteoarthritis
For patients with painful knee osteoarthritis, tai chi was as helpful as physical therapy in reducing pain and improving physical functioning, according to a new study partially funded by the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH).
NIH News in Health Feature: Science Quizzes & Puzzles
You’re invited to test your expertise and boost your science smarts by linking to more than a dozen interactive or printable crossword puzzles, quizzes, games and texts. Check out these educational resourcesfrom the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS).
EVENTS
January NIAMS Advisory Council Meeting
The NIAMS Advisory Council Meeting will be held January 25, 2017, in Building 31, 6th Floor, C Wing, Conference Room 6, NIH Campus. A meeting agenda is available. The Council meeting will be available for live viewing via the NIH videocasting service as well.

Rare Disease Day at NIH
Monday, February 27, 2017
8:30 a.m. to 4:00 p.m.
Location: NIH Campus, Masur Auditorium (Building 10)
Cost: Free
Registration is here.
Available by videocast.
NIH Wednesday Afternoon Lecture Series
The NIH’s Wednesday Afternoon Lecture Series offers weekly lectures every Wednesday at 3 p.m. in Masur Auditorium, Building 10, NIH Campus. Renowned scientists from around the globe present research on a variety of topics. The lectures are Continuing Medical Education-certified, open to the public and available live via webcast.
Upcoming Lectures:
January 25, 2017
Christine Mummery, Ph.D., Leiden University Medical Center
“Human pluripotent stem cells in understanding genetic cardiovascular disease and effects of drugs”
February 22, 2017
Dan R. Littman, M.D., Ph.D., New York University School of Medicine
“The Microbiota as Instructor and Arbiter of Immune Responses in Health and Disease”
NIH Science Lectures and Events Available via Internet
The NIH hosts a number of science seminars and events that are available online through real-time streaming video (videocast). The NIH calendar notes these videocast events with a video icon ![]() .
.
Funding Announcements
If you would like information about funding opportunities, please view the NIH Guide for Grants and Contracts, the primary source for information about NIH funding opportunities. You can also request a weekly Table of Contents from the NIH Guide. In addition, the NIAMS website provides comprehensive information on NIAMS-related grants and processes.